The health benefits of extra virgin olive oil
For many years we were told in the media and through food marketing that fat is bad for us and should be avoided at all costs, with stores offering a multitude of low-fat products from cheese to meats. However, we now know that when an element such as fat, is taken out of food, something else is added to replace that flavour and too often this was either sugar or salt, therefore bringing into questions the real health benefits of these so-called fat-free foods.
Olive oil has been a staple of the Mediterranean diet for many years, the olives are cold-pressed, and the liquid which is extracted is a lovely, thick, slightly green olive oil, that is slightly bitter to taste. When olive oil is pure, meaning it has not been refined or heated, it is known as extra virgin olive oil. However, if the label does not mention extra virgin olive oil, then you can assume that the oil has been heated and refined, which removes many of the health properties that extra virgin olive oil has to offer.
Extra virgin olive oil is now known to be part of healthy fats, as these fats do contain many health properties, which we will look at. Healthy fats are so important for our general well-being as they play a crucial role in many aspects of our health from providing us with a layer of insulation and keeping our skin waterproof, to being a key component in the production of various hormones.
Through research, we know now that although as mentioned before olive is a fat, when part of a healthy diet, it plays an important role in increasing good cholesterol (HDL) and helps to lower our bad cholesterol (LDL), it also contains many antioxidants which are very beneficial in reducing inflammation in the body. Polyphenols which are another type of antioxidant, are also found in extra virgin olive oil and it is now thought that not only can it help to improve cardiovascular health, but it can reduce the risk of developing cancer or a stroke.
Due to its anti-inflammatory properties, extra virgin olive oil has also been known to increase the microbial diversity in the gut and boost its immunity, therefore helping people suffering from digestive issues such as IBS and ulcerative colitis. These anti-inflammatory properties are not restricted to the gut but have also found to be beneficial regarding our brain health and reducing the risk of developing Alzheimer's by improving brain function.
Individuals who suffer from metabolic syndrome may benefit hugely from integrating extra virgin olive oil into their diets, as the various contributing factors such as high blood pressure, high blood sugar levels and triglycerides can be improved.
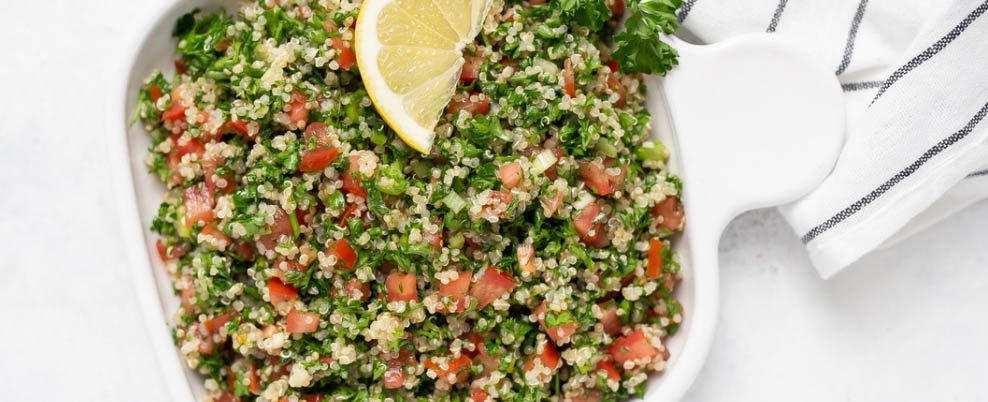
When making lifestyle and nutritional changes, olive oil is probably one of the easiest things to add to your diet. Start by making homemade salad dressing—it tastes much better than anything store-bought! You can always add some chopped herbs such as coriander, bay leaves, salt and chopped garlic. This amazing little sauce can be kept in the fridge for up to three days and it has a variety of uses, such as a dipping sauce which some fresh bread, drizzled over cooked meat, pasta or baked potatoes or simply added to a nice fresh salad. You can also use olive oil can in stir frys, or when making bread and pastry. This simple quinoa tabbouleh recipe is a great way of introducing extra virgin olive oil into your meals.
Send your nutrition questions to susan@susanalsembach.com